
Back تغذية المحيط Arabic Eisendüngung German Fertilización del océano Spanish Ookeanide väetamine Estonian Fertilisation de l'océan French
2 sequestration in the ocean
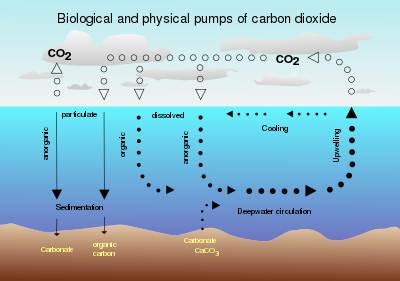
Ocean fertilization or ocean nourishment is a type of technology for carbon dioxide removal from the ocean based on the purposeful introduction of plant nutrients to the upper ocean to increase marine food production and to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.[1][2] Ocean nutrient fertilization, for example iron fertilization, could stimulate photosynthesis in phytoplankton. The phytoplankton would convert the ocean's dissolved carbon dioxide into carbohydrate, some of which would sink into the deeper ocean before oxidizing. More than a dozen open-sea experiments confirmed that adding iron to the ocean increases photosynthesis in phytoplankton by up to 30 times.[3]
This is one of the more well-researched carbon dioxide removal (CDR) approaches, however this approach would only sequester carbon on a timescale of 10-100 years dependent on ocean mixing times. While surface ocean acidity may decrease as a result of nutrient fertilization, when the sinking organic matter remineralizes, deep ocean acidity will increase. A 2021 report on CDR indicates that there is medium-high confidence that the technique could be efficient and scalable at low cost, with medium environmental risks.[4] One of the key risks of nutrient fertilization is nutrient robbing, a process by which excess nutrients used in one location for enhanced primary productivity, as in a fertilization context, are then unavailable for normal productivity downstream. This could result in ecosystem impacts far outside the original site of fertilization.[4]
A number of techniques, including fertilization by the micronutrient iron (called iron fertilization) or with nitrogen and phosphorus (both macronutrients), have been proposed. But research in the early 2020s suggested that it could only permanently sequester a small amount of carbon.[5]
- ^ Matear, R. J. & B. Elliott (2004). "Enhancement of oceanic uptake of anthropogenic CO2 by macronutrient fertilization". J. Geophys. Res. 109 (C4): C04001. Bibcode:2004JGRC..109.4001M. doi:10.1029/2000JC000321. Archived from the original on 4 March 2010. Retrieved 19 January 2009.
- ^ Jones, I.S.F. & Young, H.E. (1997). "Engineering a large sustainable world fishery". Environmental Conservation. 24 (2): 99–104. doi:10.1017/S0376892997000167. S2CID 86248266.
- ^ Trujillo, Alan (2011). Essentials of Oceanography. Pearson Education, Inc. p. 157. ISBN 9780321668127.
- ^ a b National Academies of Sciences, Engineering (8 December 2021). A Research Strategy for Ocean-based Carbon Dioxide Removal and Sequestration. doi:10.17226/26278. ISBN 978-0-309-08761-2. PMID 35533244. S2CID 245089649.
- ^ "Cloud spraying and hurricane slaying: how ocean geoengineering became the frontier of the climate crisis". The Guardian. 23 June 2021. Archived from the original on 23 June 2021. Retrieved 23 June 2021.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search